Describe the Metabolic Response to Starvation
During starvation the body is faced with an obligate need to generate glucose to sustain cerebral energy metabolism100g of glucose per day. We describe how the body adapts to decreased nutrient supply increased energy demands and to stress.

Undernutrition Simple And Stress Starvation
METABOLIC STRESS STARVATION What is Metabolic Stress.

. Starvation for a long time will cause a metabolic shift in that our body uses fat as an energy source instead of glucose. Glycerol and gluconeogenic amino acids - glucose. On average the starvation response of the individuals after isolation was a 180 kCal reduction in daily total energy expenditure.
Decline in metabolic rate Refeeding syndrome involves physiologic and metabolic. Many patients are malnourished have impaired exercise tolerance or undergo the stress response. Metabolic traits respond readily to ambient temperature variation in some cases increasing relative or absolute energetic.
Energy metabolism covers various biochemical ways of energy transformation and regulation of thousands of chemical reactions. The bodys response to stress can be summarized by. View the full answer.
Starvation seriously alters the metabolic functions of our body. Ebb and Flow phases Trauma causes major alterations in energy and protein metabolism. Use of muscles for glucose in brain then fatty acid chains -- brain needs 100 grams of carbs ketone body production from fatty acid stores.
60 kCal of the starvation response was explained by a reduction in fat-free mass and fat mass. Without fine regulation of those metabolic processes cells and organisms cannot maintain activities linked to life. The differences between lean and obese subjects have important physiologi- cal implications some of which are of obvious relevance to survival.
During severe stress the bodys metabolic rate rises profoundly thus becoming hypermetabolic. Starvation exercise and the stress response have a physiological impact on the body. Body uses stored energy as fuel when dietary intake.
The metabolic response to trauma in humans has been defined in 3 phases. Disturbances in energy metabolism include starvation and diabetes. Adptation of body to fasting PHYSIOLOGICAL ADAPTATION.
It will be very useful for Final year MBBS students. The remaining 55 kCal was statistically insignificant. Provision of at.
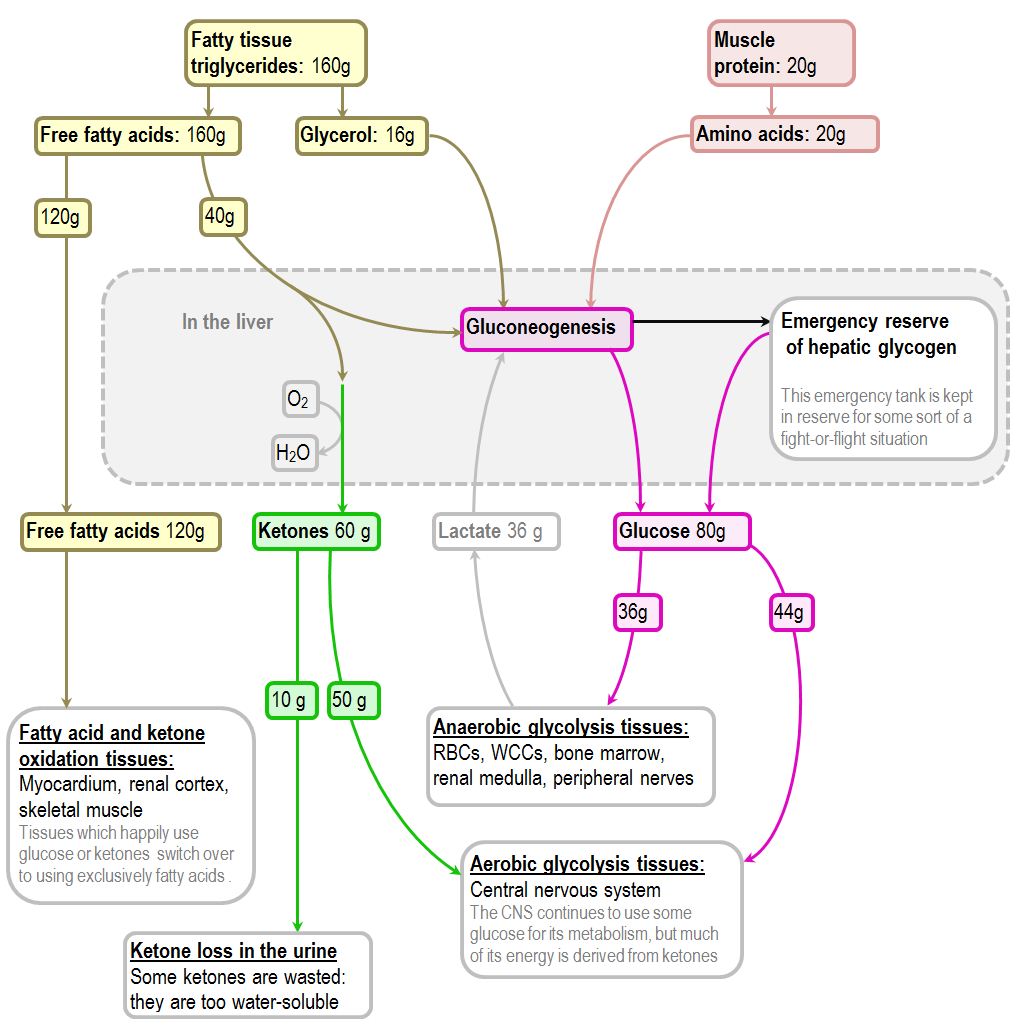
Metabolic rate and the flexibility thereof is a complex trait involving several inter-linked variables that can influence animal energetics behavior and ultimately fitness. During starvation most tissues utilise fatty acids andor ketone bodies to spare glucose for the brain. Initially stores of carbohydrate precursors eg.
High concentrations of ketone bodies result in significant excretion of ketones. The response to trauma can be divided into the ebb phase and the flow phase. Describe the metabolic response to starvation.
The metabolic response to sepsis entails rapid breakdown of the bodys reserves of protein carbohydrate and fat. The metabolic response to starvation is characterised by a switch from carbohydrate metabolism to fat cmetabolism in. The ebb phase occurs immediately after trauma and lasts.
B Compare and contrast the metabolicbiochemical response to the energy metabolism disturbances caused by starvation and diabetes. Decreased insulin increased glucagon - increased hepatic glycogenolysis gluconeogenesis amino acid uptake ureagenesis protein catabolism. Flatt Biology Diabetes 1972 TLDR.
Additional MNT Considerations Short term starvation. It is no longer acceptable to describe the metabolic response to starvation as a single typical response and the differences between lean and obese subjects have important physiological implications some of which are of obvious relevance to survival. The postoperative changes in energy metabolism thermo-regulation and fluid and energy requirements vary between newborns children and adults 6.
Briefly the human body response to starvation at a cellular level results in a reduced metabolic rate and a switching of food supply for various cells. Glycogen - glucose under action of glucose-6-phosphatase. Bodys response to metabolic stress Nutrition Diagnoses What are possible nutrition diagnoses for metabolic stress.
Avoidable Factors Starvation. The human body switches from burning carbohydrates to fat to maintain the blood glucose levelAt the time of starvation the plasma level of fatty acids and ketone bodies. It is no longer acceptable to describe the metabolic response to starvation as a single typical response.
Get started for FREE Continue. An additional 65 kCal was explained by a reduction in fidgeting. Starvation Use of stored carbohydrate fat and protein to meet energy demands Liver glycogen Fatty acid stores Gluconeogenesis Glucose needed for brain and red blood cells Lean body mass protein and glycerol portion of triglycerides will be used instead.
The metabolic response of the body to the starvation is important and is characterised by transmission to fat metabolism from carbohydrate metabolismThis is happened in the low metabolic state. A Describe how the body and brain remain fueled for both energy and glucose during starvation over time early middle late. This 7 week-course will give you a clear introduction to the basic fundamentals of energy metabolism.
Glucose utilisation by the brain is decreased during prolonged starvation as the brain utilises ketone bodies as the major fuel. Ketones are produced from fatty acids. The normal protein- and energy-conserving mechanisms evoked during simple starvation are not observed following the onset of sepsis.
This PPT describes about the Metabolic response to injury as given in Bailey Love - 26th edition. During starvation the bodys metabolic rate slows becoming hypometabolic. Ebb phase or decreased metabolic rate in early shock phase Flow phase or catabolic phase Anabolic phase if the tissue.
Then in the first 24-48 hours there is increased gluconeogenesis from amino acids and glycerol. Glucose is a primary cellular food source used by all cells in the body. Human starvation protein carbohydrate fat ketone bodies.
82 PDF On the Maximal Possible Rate of Ketogenesis J.
Physiological Adaptation To Prolonged Starvation Deranged Physiology

No comments for "Describe the Metabolic Response to Starvation"
Post a Comment